Ceramic magnets, also called ferrite core magnets, are hard and permanent magnets with low costs. The composition of ceramic magnets includes iron oxide and strontium carbonate. They exhibit medium magnetic strength and can be used at fairly high temperatures. Read More…
Founded in 1895, Arnold Magnetic Technologies is a leading global manufacturer of high performance permanent magnets, electromagnetics, magnetic assemblies, and precision thin metals.
At Applied Magnets, we are dedicated to providing some of the most powerful and reliable magnets available on the market. We specialize in high-grade neodymium magnets which are widely recognized for their unmatched strength and efficiency across a broad range of applications. From advanced engineering projects and industrial machinery to consumer products, scientific research, and educational...

Our customers know they can trust us to provide them with the best magnets in the industry. We supply magnets from only the best manufacturers in the world. We will not offer substandard products or anything that is not the most cost-effective solution.
At TyTek Industries, we are experts in manufacturing magnetic components. Our magnetics catalog include magnetic assembly, alnico magnets, rare earth magnets, and many more. It is our team’s mission to always draw on our strengths and experience to ensure the very best service and quality for our customers. For more information, visit our website or call today!

Magnetic Specialties is a magnet manufacturer of magnet tools for the lifting & handling of materials & parts, industrial recycling and material separation applications. Products include magnetic grates, overhead magnets, tilting magnets, plate magnets, magnetic pulleys, magnetic drums and hoist magnets.
More Ceramic Magnet Manufacturers
What are Ceramic Magnets?
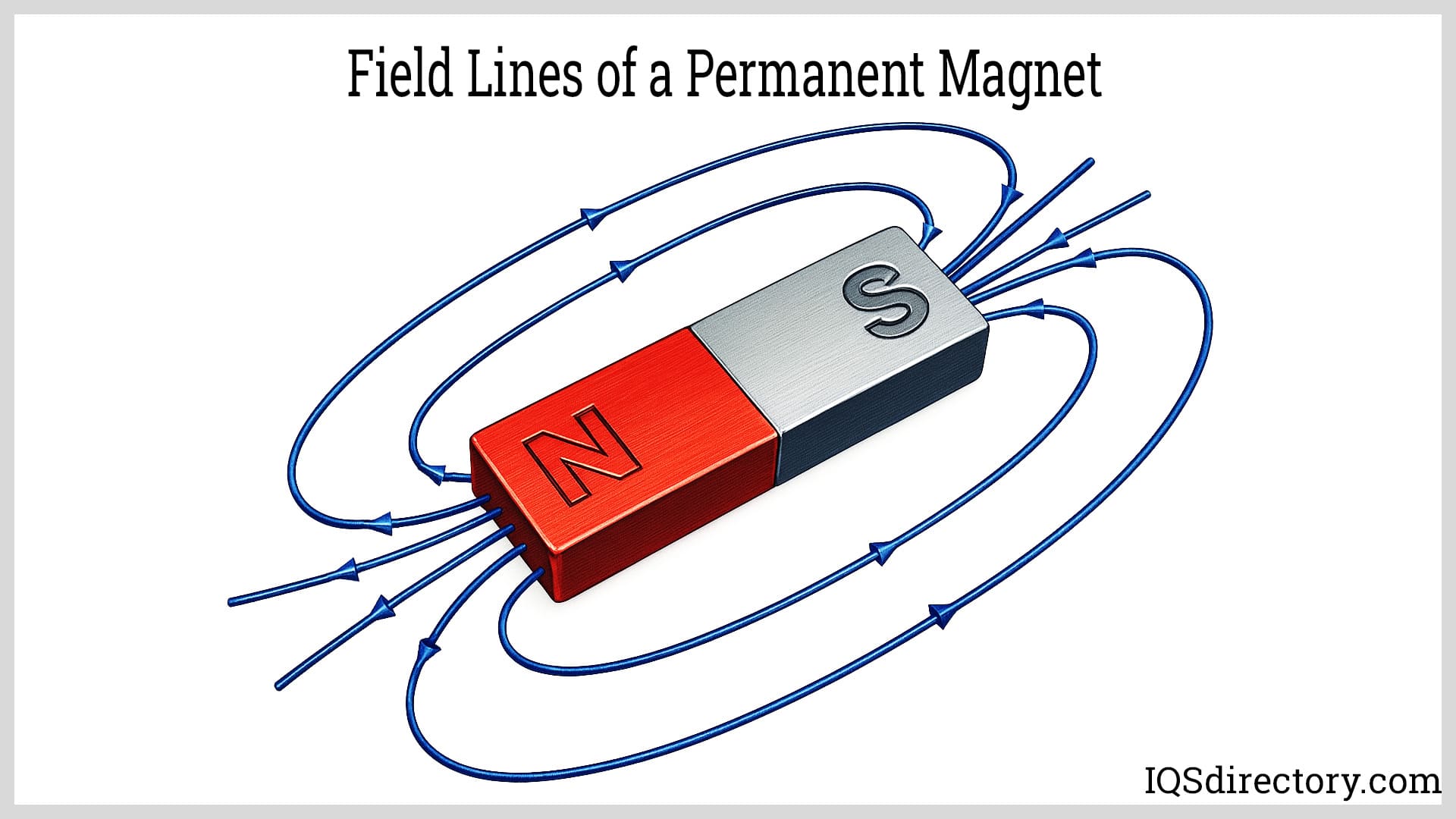
Ceramic magnets, also known as ferrite magnets, are a widely used type of permanent magnet that offer excellent resistance to oxidation and corrosion. Unlike neodymium or samarium cobalt magnets, ceramic magnets typically do not require additional protective coatings or finishes, making them ideal for use in harsh environments and industrial applications. Their robust nature and ease of magnetization make ceramic magnets a popular choice for manufacturers, engineers, and consumers in a wide variety of industrial, commercial, technical, and consumer electronics applications.
Available in a diverse range of shapes and sizes—including block (rectangular and square), disc, round cup, ring magnets, and custom configurations—ceramic magnets are versatile and adaptable for numerous design requirements. Their cost-effectiveness, combined with reliable magnetic performance, positions ceramic magnets as a leading solution for both high-volume manufacturing and specialized projects.

Chemical Composition of Ceramic Magnets
At the core of ceramic magnets is the chemical compound ferrite, composed primarily of iron oxide (Fe2O3) and one or more additional metallic elements. The most common composition is SrO-6(Fe2O3), indicating a mixture of strontium oxide and iron oxide. This precise blend results in a hard, brittle material with strong magnetic properties. Ferrite magnets are classified as either strontium ferrite or barium ferrite, depending on the specific raw material used.
To produce ceramic magnets, manufacturers typically combine iron oxide (90%) and strontium carbonate (10%) or barium carbonate. These raw materials are abundant and economically viable, contributing to the low production cost of ceramic magnets compared to rare earth magnets. The use of cost-effective materials makes ceramic magnets an attractive option for mass production and budget-sensitive projects without compromising magnetic strength in many standard applications.
The Manufacturing Method of Ceramic Magnets
The manufacturing process of ceramic (ferrite) magnets involves several precise steps to ensure optimal magnetic properties and dimensional accuracy. Below is an overview of the key stages:
- Raw Material Preparation: The process begins by blending iron oxide with strontium or barium carbonate. These materials are calcined, or heated, to form a homogeneous metallic oxide mixture.
- Milling: The calcined product undergoes multiple milling operations to reduce it to a fine powder. The particle size achieved during milling influences the final magnet's performance.
- Compaction: There are two main methods for compacting the powder in a die:
- Dry Pressing: The powder is compacted without any liquid binder, resulting in an isotropic magnet. Isotropic ceramic magnets have uniform magnetic properties in all directions, though they tend to be slightly weaker magnetically but easier to manufacture with tighter dimensional tolerances. Often, dry-pressed magnets do not require additional grinding.
- Wet Pressing (Anisotropic): The powder is mixed with water to form a slurry and compacted in a die within a magnetic field. The applied field orients the grains, producing an anisotropic magnet with superior magnetic strength in a specific direction. Wet-pressed magnets typically require post-sintering grinding to achieve precise dimensions.
- Sintering: The compacted parts are sintered at high temperatures, usually between 1000°C and 1300°C, to achieve the final fusion of particles and develop the desired magnetic characteristics. Sintering also imparts the hard, brittle nature characteristic of ceramic magnets.
- Finishing: Diamond abrasives or other specialized grinding tools shape the sintered magnets to their final dimensions, ensuring tight tolerances and optimal performance for the intended application.
Frequently Asked Manufacturing Questions
- How does the manufacturing process influence the strength of ceramic magnets? The use of an applied magnetic field during wet pressing aligns the magnetic domains, producing stronger, anisotropic magnets suitable for demanding industrial applications.
- Are custom shapes and sizes available? Yes, many ceramic magnet manufacturers offer custom fabrication to meet unique size, shape, and performance requirements. Contact a ceramic magnet supplier to discuss your project specifications.
- What industries benefit most from ceramic magnets? Automotive, electronics, consumer products, medical devices, renewable energy, and educational sectors frequently utilize ceramic magnets due to their cost-effectiveness and versatility.
Types of Ceramic Magnets
Ceramic magnets can be categorized based on their composition, magnetic properties, and intended applications. Understanding the different types can help buyers and engineers select the right magnet for their specific requirements:
Ceramic Permanent Magnets (Hard Ferrites)
Ceramic permanent magnets, also called hard ferrites, are the most recognizable form—commonly seen as small black magnets. These magnets are manufactured from barium carbonate, strontium carbonate, and iron oxide. Once magnetized, they retain their magnetic field for extended periods, making them ideal for use in applications where stable, long-term magnetic force is required. Their resistance to demagnetization and corrosion further enhances their suitability for rugged environments.

Soft Ceramic Magnets (Soft Ferrites)
Soft ceramic magnets, or soft ferrites, are produced by sintering ferric oxide with one or more metal oxides, such as zinc oxide, strontium oxide, barium oxide, magnesium oxide, manganese oxide, or nickel oxide. These magnets have low coercivity, meaning their residual magnetic field becomes negligible once the external magnetic field is removed. Soft ferrites are primarily used as cores in transformers, inductors, chokes, and other electronic devices that require rapid switching of magnetic fields without significant energy loss.

Compared to permanent ceramic magnets, soft ferrites are invaluable for applications involving alternating current (AC) and high-frequency circuits, such as radio frequency (RF) transformers and electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression components.
Gyromagnetic Ceramic Magnets
Gyromagnetic ceramic magnets are specialized ferrite materials exhibiting gyromagnetic properties. These properties allow the polarization plane of electromagnetic waves to rotate as they propagate through the material, a phenomenon crucial for various microwave communications technologies. Under the influence of perpendicular DC and electromagnetic wave magnetic fields, these magnets demonstrate controlled rotary magnetism, making them essential for devices such as microwave isolators, circulators, and phase shifters in telecommunications and radar systems.
Other Specialized Ceramic Magnet Types
- Flexible Ceramic Magnets: Created by binding ferrite powder with a flexible rubber or polymer matrix, these magnets can be cut, shaped, and bent, making them ideal for signage, labels, and educational tools.
- High-Energy Ceramic Magnets: Engineered for applications demanding higher magnetic field strength, these magnets use advanced processing techniques to maximize energy product while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Applications and Benefits of Ceramic Magnets
Ceramic magnets are valued for their performance, durability, and affordability across an array of industries. Below is a comprehensive overview of common applications and key benefits to help you determine if ceramic magnets are the right choice for your project:
Applications of Ceramic Magnets
- Magnetic assemblies designed for holding, lifting, retrieving, and separating ferrous materials in manufacturing, recycling, and construction industries
- Guitar pickups and audio equipment, where consistent magnetic fields ensure reliable sound reproduction
- Brakes and clamps in mechanical and automotive systems
- Electrical relays and switches, leveraging the magnets' stable properties for control systems
- Motors and generators for both consumer appliances and industrial machinery
- Eddy current devices used in non-destructive testing and metal detection
- Loudspeakers and headphones for clear, powerful audio output
- Educational and school projects, including science experiments and demonstrations of magnetic principles
- Security systems, such as magnetic door sensors and alarm contacts
- Crafting projects and hobbyist model making, where easy customization is a benefit
- Fridge magnets and promotional items
- Medical devices (in non-critical, low-risk applications)
- Renewable energy projects, including basic magnetic couplings and small wind turbine generators
Benefits of Ceramic Magnets
- Low Production Cost: Ceramic magnets are among the most economical permanent magnets, making them ideal for large-scale manufacturing and budget-sensitive applications.
- High Intrinsic Coercivity: Their resistance to demagnetization from external magnetic fields surpasses that of Alnico magnets, ensuring reliable performance in challenging conditions.
- High Magnetic Permeability: Ceramic magnets can store strong magnetic fields, outperforming many metallic magnets in certain applications.
- Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance: Their intrinsic material properties eliminate the need for additional protective coatings, making them suitable for outdoor and industrial use.
- Versatile Shapes and Sizes: The manufacturing process enables the creation of simple or complex geometries tailored to specific requirements.
- Stable Performance Over Time: Ceramic magnets retain their magnetic properties for years, providing long-term value and dependability.
- Lower Service Temperature: While their operational temperature is lower than some rare earth magnets, ceramic magnets maintain stability in most ambient conditions found in everyday environments.
- Environmental Friendliness: Made from abundant, non-toxic materials, ceramic magnets are a sustainable choice for eco-conscious buyers.
Limitations to Consider
- Brittleness: Ceramic magnets are hard but brittle and can break or chip if handled improperly or subjected to impact.
- Lower Maximum Energy Product: Compared to neodymium magnets, ceramic magnets provide lower maximum energy, which may not suit applications requiring extremely high magnetic force in compact sizes.
- Not Suitable for High-Temperature Applications: Service temperatures typically max out around 250°C (482°F).
Use Case Scenarios
Wondering whether ceramic magnets are the right fit for your project? Consider the following popular scenarios:
- Need a cost-effective magnet for general industrial use? Ceramic magnets offer reliable performance for holding, lifting, and separation tasks at a fraction of the cost of rare earth magnets.
- Designing educational kits or science projects? Their safety, affordability, and ease of use make ceramic magnets the top choice for teachers and students.
- Building consumer electronics or automotive parts? Ceramic magnets are widely used in motors, sensors, and actuators due to their durability and stable magnetic properties.
- Seeking magnets for outdoor or corrosive environments? Take advantage of ceramic magnets' natural resistance to rust and oxidation.
Comparing Ceramic Magnets to Other Magnet Types
When selecting magnets, you may wonder: How do ceramic magnets compare to neodymium, samarium cobalt, or Alnico magnets? Here’s a quick overview to guide your buying decision:
| Magnet Type | Cost | Maximum Energy Product (BHmax) | Corrosion Resistance | Temperature Stability | Brittleness | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic (Ferrite) | Low | Moderate | High | Good (to 250°C) | High | Motors, speakers, holding devices |
| Neodymium (NdFeB) | High | Very High | Low (needs coating) | Moderate (to 80–200°C) | High | Miniature motors, sensors, electronics |
| Samarium Cobalt (SmCo) | Very High | High | Very High | Excellent (to 350°C) | High | Aerospace, military, high-temp |
| Alnico | Moderate | Moderate | High | Excellent (to 500°C) | Low | Instruments, sensors, vintage electronics |
Still unsure which magnet type is best for your needs? Ask yourself:
- Do you need maximum magnetic strength in a very small size (choose neodymium)?
- Are you working in a high-temperature or corrosive environment (consider samarium cobalt or Alnico)?
- Is cost a primary driver and moderate magnetic strength sufficient (ceramic magnets are your answer)?
Choosing the Right Ceramic Magnets Manufacturer
To ensure the most productive outcome when purchasing ceramic magnets, it's essential to choose a reputable and experienced ceramic magnet manufacturer or supplier. Here are some tips to help you make an informed decision:
- Compare Multiple Ceramic Magnet Suppliers: Evaluate at least six different ceramic magnet manufacturers by reviewing their business profiles, capabilities, and customer feedback. This helps you identify the supplier best suited to your project's specifications.
- Assess Technical Expertise: Look for suppliers with experience in producing both standard and custom ceramic magnets, including isotropic and anisotropic variants, and those who can advise on material selection and manufacturing methods.
- Request Samples and Data Sheets: Before committing to a large order, ask for product samples or detailed technical data. This ensures the magnets meet your required performance criteria, such as pull force, operating temperature, and tolerance.
- Evaluate Manufacturing Capabilities: Does the supplier offer value-added services such as machining, coating, or magnet assembly? Are they equipped to handle high-volume production or rapid prototyping?
- Use Online Tools: Our platform provides comprehensive business profiles, a patented website previewer, and a streamlined RFQ (Request for Quote) form to quickly contact multiple ceramic magnet suppliers with your project requirements.
Ready to find the best ceramic magnet manufacturer for your needs? Start by:
- Reviewing company websites and business profiles for expertise and product offerings
- Using our RFQ tool to request quotes from multiple suppliers simultaneously
- Directly contacting manufacturers with your custom magnet specifications
- Asking about technical support, lead times, and minimum order quantities
Frequently Asked Buying Questions
- What factors should I consider when choosing a ceramic magnet supplier? Look for experience, product range, customization capabilities, quality certifications, and responsive customer service.
- Can I order custom-shaped or sized ceramic magnets? Yes, most manufacturers welcome custom orders and can assist with engineering support for unique applications.
- How do I evaluate the quality of ceramic magnets? Request technical data sheets, ask about quality assurance processes, and consider ordering samples for testing in your application.
Get Started: Find a Trusted Ceramic Magnet Supplier
Whether you need standard ferrite magnets for bulk manufacturing, custom ceramic magnetic assemblies for specialized equipment, or expert guidance on material selection, our network of verified ceramic magnet manufacturers is ready to assist. Start your search today and connect with top industry suppliers for all your ceramic magnet needs.
Have more questions? Looking for technical support or design guidance? Contact our team for personalized assistance in selecting and sourcing the ideal ceramic magnets for your next project.








 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers Aluminum
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Magnets
Magnets Nickel
Nickel Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services